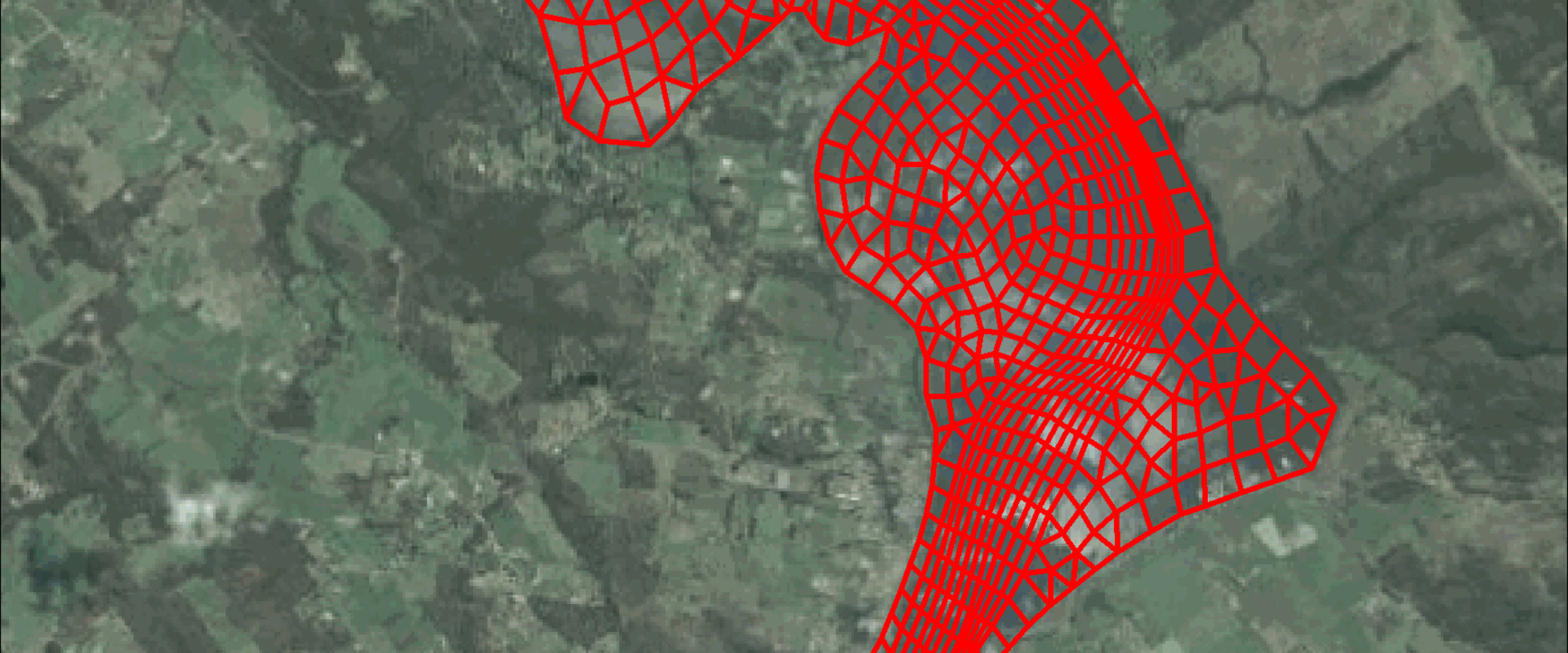
Three Dimensional Modelling of the Tamar River
We were commissioned to develop a three dimensional hydrodynamic, sediment transport and water quality model of the Tamar River, Tasmania.
Customer: NRM North
The Tamar River has experienced significant environmental changes over several decades, primarily as a result of anthropogenic impacts such as upstream damming, catchment development, and direct delivery of urban wastewater to poorly flushed river reaches.
As a result, the river exhibits degraded sediment and water quality conditions in most upstream reaches that require active intervention to remediate.
We were commissioned to develop a numerical model to support the development of such intervention strategies.
The model was used successfully to investigate the potential effectiveness of a range of structural and environmental alterations to the estuary. Some scenarios showed marked improvement in places, but with deleterious consequences elsewhere.
The model was able to be used to quantify these benefits and consequences and provide robust predictions of overall environmental benefits.
The modelling tool can be continually refined and used to assist in ongoing management decisions.

BMT has developed a comprehensive model for analysing the impacts on morphological processes of the Murray River mouth and associated water levels and salinity levels throughout Coorong and Lower Lakes resulting from variable river flows and release strategies at the barrages, incorporating ocean tide, storm surge, wave and wind processes.

We developed a 3D hydrodynamic and water quality model of the region around the Abrolhos Islands in Western Australia. In collaboration with the University of Western Australia, model results were used to assess the impact of proposed finfish aquaculture on the surrounding environment.

We were contracted by TOTAL (Paris) to undertake cooling water discharge modelling studies on behalf of Shtokman Development AG.

The proposed expansion of the Port of Townsville involves significant dredging of sea bed materials to provide for vessel access, maneuvering and berthing.